Trainable Noise Model as an XAI evaluation method: application on Sobol for remote sensing image segmentation
Abstract
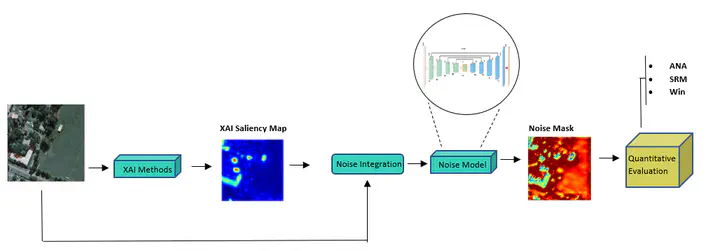
eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has emerged as an essential requirement when dealing with mission-critical applications, ensuring transparency and interpretability of the employed black box AI models. XAI significance spans various domains, from healthcare to finance, where understanding the decision-making process of deep learning algorithms is essential. Most computer vision AI-based models are often black boxes; hence, providing explainability of image processing deep neural networks is crucial for their wide adoption and deployment in medical image analysis, autonomous driving, and remote sensing applications. Existing XAI methods aim to provide insights about the methodology used by the black box model in making decisions by highlighting the most relevant regions within the input image that contribute to the model’s prediction. Recently, several XAI methods for image classification tasks have been introduced. On the contrary, image segmentation has received comparatively less attention in the context of explainability, even though it is a fundamental task in computer vision applications, especially in remote sensing. Only some research proposes gradient-based XAI algorithms for image segmentation. This paper adapts the recent gradient-free Sobol XAI method for semantic segmentation. To measure the performance of the Sobol method for segmentation, we propose a quantitative XAI evaluation method based on a learnable noise model. The main objective of this model is to induce noise on the explanation maps, where higher induced noise signifies low accuracy and vice-versa. A thorough benchmark is conducted using high-resolution satellite images focusing on buildings’ segmentation tasks. Our results reveal that the proposed noise-based evaluation technique can effectively compare the fidelity of different XAI methods.