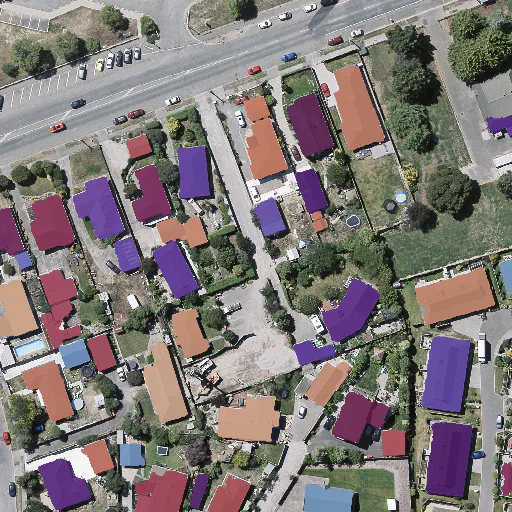
GeoUrban-AI Tool
GeoUrban-AI powered [Tool] allows to autonomously extract buildings' footprints from satellite/aerial imagery. The aim is to make our applied research findings accessible to a larger community. Though it is not common to develop such a web-based tool for a team that is mainly involved with research rather than product development; We believe this demo would help us target a larger audience and would open up new horizons for the GEOAI group.
Automated National Urban Map Extraction
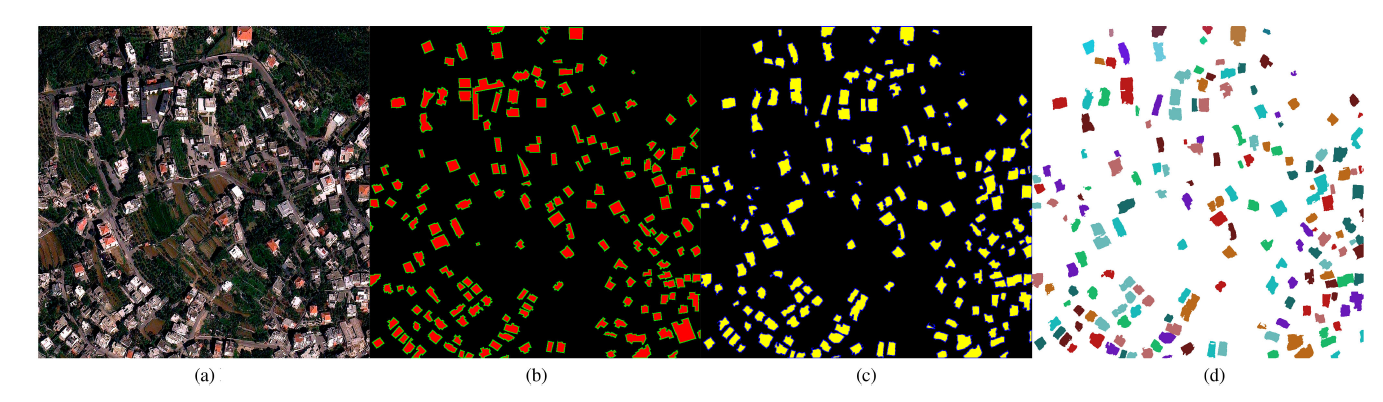
Developing countries usually lack the proper governance means to generate and regularly update a national rooftop map. Using traditional photogrammetry and surveying methods to produce buildings map at the federal level is costly and time-consuming. Relying on earth observation and deep learning methods, we aim in this project to bridge this gap and propose a pipeline to autonomously produce national urban maps. We detail all engineering steps to replicate this work and ensure highly accurate results in dense and slum areas witnessed in regions that lack proper urban planning in the Global South. We applied a case study of the proposed pipeline to Lebanon and successfully produced the first comprehensive national building footprint map with approximately 1 Million units with an 84% accuracy. The proposed architecture relies on advanced augmentation techniques to overcome dataset scarcity, which is often the case in developing countries.
[Map] encompases ~1 MM urban units with an 84% accuracy. When you ZOOM IN, the dots on the map refer to the centroids of each building at a specific geographical location [Paper]
.
Solar Potential Map for Lebanon
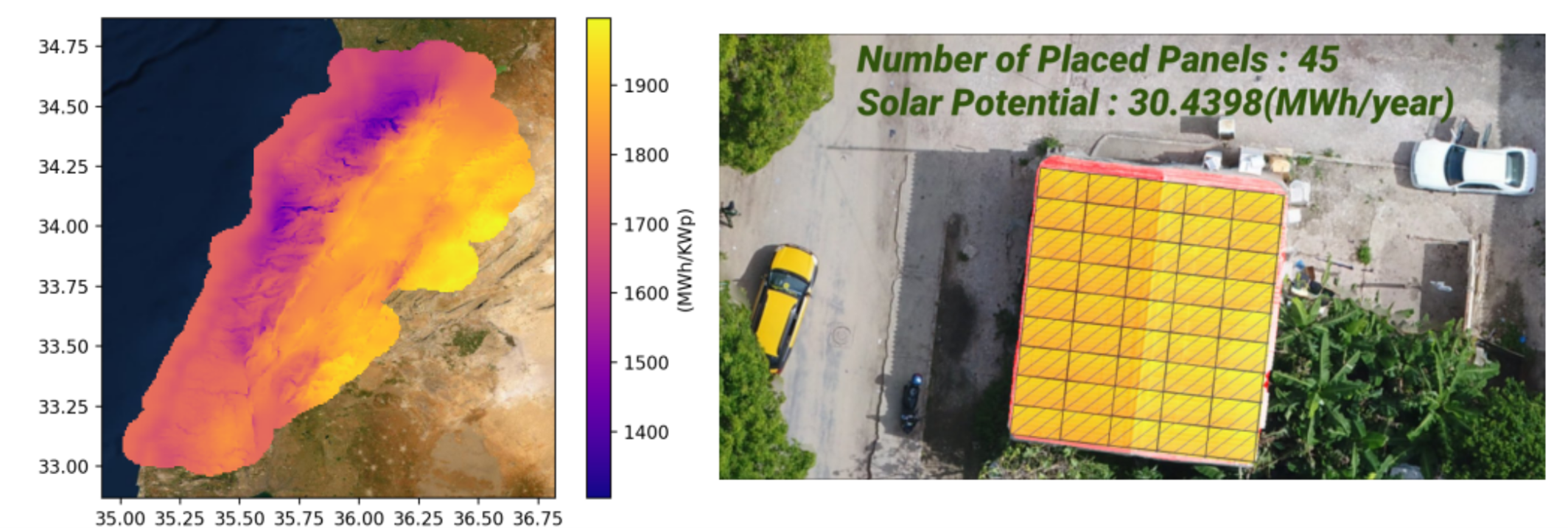
Estimating the solar potential of buildings' rooftops at a large scale is a fundamental step for every country to utilize its solar power efficiently. However, such estimation becomes time-consuming and costly if done through on-site measurements. This project uses deep learning-based multi-class instance segmentation to extract buildings' footprints from satellite images. We propose a photovoltaic panels placement algorithm to estimate the solar potential of every rooftop, which results in Lebanon's first buildings' solar potential map. We report average and total solar potential per district and localize regions corresponding to the highest solar potential yield [Paper].
Sci-Net: a Scale Invariant Model for Building Detection from Aerial Images
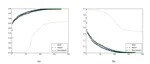
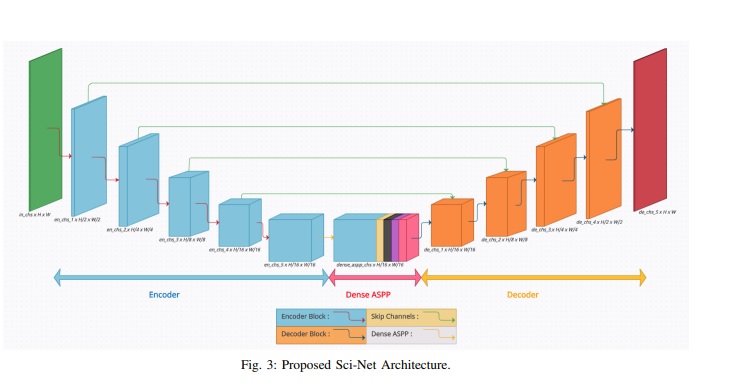
Buildings’ segmentation is a fundamental task in the field of earth observation and aerial imagery analysis. Most existing deep learning based algorithms in the literature can be applied to fixed or narrow-ranged spatial resolution imagery. In practical scenarios, users deal with a wide spectrum of images resolution and thus, often need to resample a given aerial image to match the spatial resolution of the dataset used to train the deep learning model. This however, would result in a severe degradation in the quality of the output segmentation masks. To deal with this issue, we propose in this research a Scale-invariant neural network (Sci-Net) that is able to segment buildings present in aerial images at different spatial resolutions. Specifically, we modified the U-Net architecture and fused it with dense Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) to extract fine-grained multi-scale representations. We compared the performance of our proposed model against several state-of-the-art models on the Open Cities AI dataset, and showed that Sci-Net provides a steady improvement margin in performance across all resolutions available in the dataset [Paper].
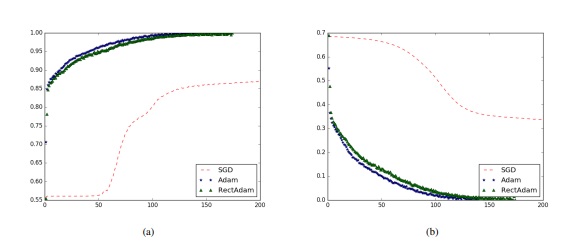
Buildings Classification using Very High Resolution Satellite Imagery
Buildings classification using satellite images is becoming more important for several applications such as damage assessment, resource allocation, and population estimation. This project focuses on two specific classification tasks: building-type classification (residential or non-residential) and building-damage assessment (damaged or not-damaged). We propose to rely solely on RGB satellite images and follow a 2-stage deep learning-based approach. Due to the lack of an appropriate dataset for the residential/non-residential building classification, we introduce a new dataset of high-resolution satellite images. We conducted extensive experiments to select the best hyper-parameters, model architecture, and training paradigm, and we propose a new transfer learning-based approach that outperforms classical methods [Paper].